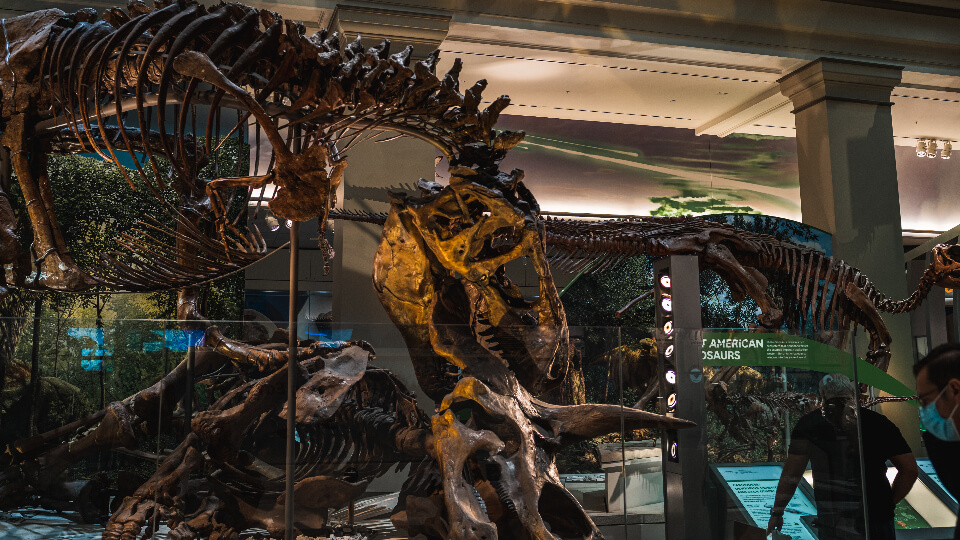Leveraging RFID technology, archaeologists can record and track every precious artifact in real time with accuracy, thereby greatly enhancing on-site operational efficiency and data management precision.
Digital Archaeology
In a dinosaur fossil excavation on an American Indian reservation in South Dakota, the archaeological team employed RFID tag technology to digitize 347 ancient artifacts. Among these were 70 Edmontosaurus fossils. By affixing passive UHF RFID tags to each fossil, the team was able to record data in real time for every stage of the process—including collection, transportation, storage, and display. According to reports, by utilizing this system, the on-site data collection time was “reduced by 80%” while the accuracy of fossil data was “nearly 100%.”
Traditional archaeology has relied on pen-and-paper recording, which often leads to incomplete information due to scattered records or lost notes. RFID technology, however, changes this scenario. Once a fossil is discovered, its detailed description, photographs, and GPS location are scanned using a handheld reader and entered into the system, then associated with the RFID tag’s unique identification number (EPC). This process creates a complete digital archive for each artifact.
By attaching a passive UHF RFID tag to each artifact, the system significantly improves on-site workflows, making the collection and management of fossil data much more efficient.
Real-Time Tracking and Precise Management
RFID technology not only greatly increases the efficiency of data collection on site but also enables the archaeological team to achieve real-time tracking throughout the entire lifecycle of the fossils. From excavation and on-site processing to warehouse storage and subsequent exhibition, RFID tags continuously record the status and location of each artifact.
This multidimensional data integration advantage allows archaeological experts to not only know the precise current location of a fossil in real time but also to update and review its historical record at any time, providing strong data support for further research.
A Leap in Archaeological Workflow Efficiency
The introduction of RFID tag technology has greatly simplified on-site archaeological operations. With the help of RFID identification and related solutions, operations that once took 20 to 30 minutes can now be completed in just two to three minutes.
This increase in efficiency not only saves a significant amount of manpower and time at the excavation site but also lays a solid foundation for subsequent data collation, artifact conservation, and exhibition preparation. Particularly in remote areas with weak network signals and harsh conditions, the RFID system supports offline data collection and automatically synchronizes when connectivity is restored, ensuring data integrity and continuity.

Broad Prospects for Cross-Disciplinary Applications
Although the application of RFID technology in archaeology has already achieved significant results, its actual deployment still faces some challenges. For example, the differences in material composition among fossils require the archaeological team to select different types of tags. Additionally, unstable network connectivity in remote excavation sites poses certain difficulties for data synchronization. Experts are actively exploring more comprehensive solutions to these issues.
When faced with fossils of different materials, it is essential to flexibly choose the appropriate RFID tags. For those areas with weak network connections, the system’s offline data collection function guarantees that data will not be lost.
In the future, as RFID technology continues to mature and integrates more deeply with GIS, the Internet of Things, big data, and other technologies, its application prospects in both archaeology and the broader field of cultural heritage conservation will become even wider. Experts are also actively discussing how to extend this technology to more types of excavation sites and artifact management projects, aiming to achieve digital archaeological management on a global scale.