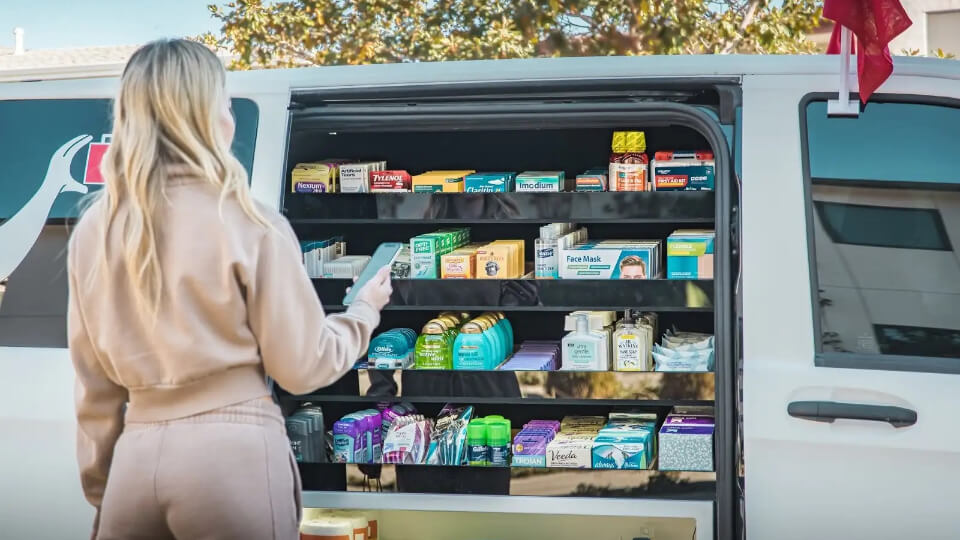
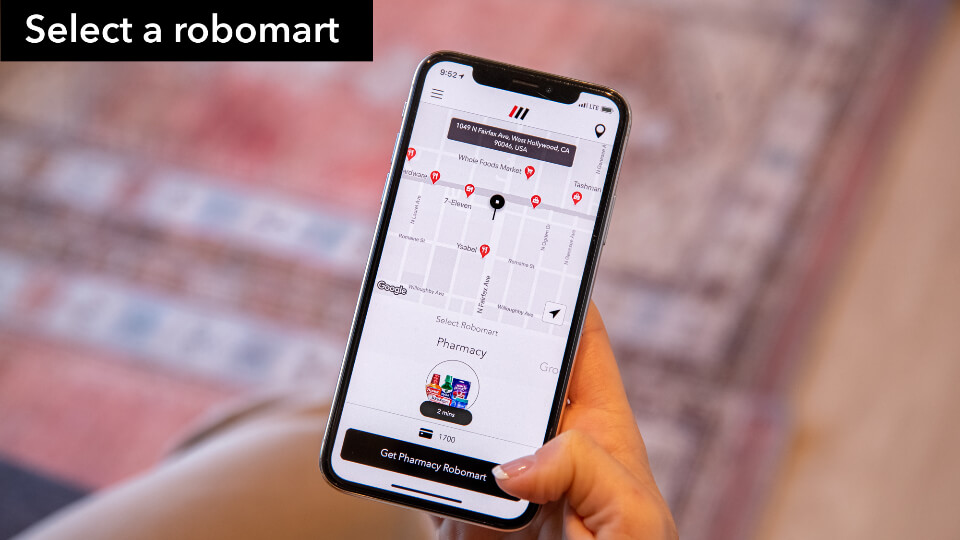
In 2024, the smart store manufacturing company Robomart, in collaboration with partners Whale Dynamic, Avery Dennison Smartrac, Zeeba, and PIX Moving, established the Autonomous Retail Collective (ARC) to promote self-driving stores based on RFID technology. This system is summoned via a mobile app, and the store autonomously drives to the user’s location within 10 minutes. Once unlocked, users can enter the mobile store to browse and select products at their leisure. The system utilizes built-in RFID readers to monitor in real time the status of every item equipped with a passive UHF RFID tag, automatically completing the checkout process. The entire shopping experience is seamless and highly convenient.
Since launching pilot projects such as Snacks Robomart and Pharmacy Robomart in California in 2021, Robomart’s application has demonstrated a 90% repeat purchase rate and an average of 2.3 orders per week. This success clearly indicates the significant advantages of this new retail model in enhancing consumer convenience while reducing operating costs.
1. Principles of Self-Driving Stores
RFID technology enables contactless data exchange through wireless radio frequency signals and consists primarily of three components: tags, readers, and antennas. In self-driving stores, every product is embedded with or affixed with an RFID tag that stores a unique code along with product information. The reader emits an electromagnetic field through its antenna to activate the tag and read its data, which is then transmitted to a back-end system for processing. This technology overcomes the limitations of traditional barcodes that require line-of-sight scanning, as it supports batch reading of multiple tags and penetrative identification, thereby significantly enhancing product tracking efficiency.
The system architecture of self-driving stores typically includes the following modules:
RFID Tagging and Product Management: Every product is equipped with a passive RFID tag, which is cost-effective and requires no battery since it draws power through electromagnetic induction to transmit data.
Intelligent Sensing Network: Multiple readers and antennas are deployed throughout the store. By integrating AI algorithms, the signal coverage is optimized to ensure comprehensive, dead-zone-free identification.
Automated Checkout System: When consumers exit the store, the readers at the access points automatically scan the product tags and complete the payment via the linked payment account, offering an “instant take-and-go” experience.
Dynamic Replenishment and Inventory Management: Real-time data monitoring of shelf status is combined with self-driving robots or drones to automate the replenishment process, reducing the need for manual intervention.
2. Application Scenarios and Model Innovations
In these stores, consumers can freely enter and exit without the need for identity verification, as the product tags are directly linked to the checkout system. For instance, Alibaba’s Hema Fresh employs RFID technology to create a fast-track checkout channel, where the system automatically identifies products and deducts payment as consumers leave.
By integrating AI with SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) technology, shopping carts can automatically follow users and update the shopping list in real time via built-in RFID readers. Additionally, users can query product information through voice interaction, thereby enhancing shopping efficiency.
Self-driving technology also endows the store with mobility. For example, unmanned delivery trucks or robots equipped with shelves can dynamically reposition themselves in specific areas (such as communities or business districts), effectively providing targeted service by bringing products directly to consumers.
3. Advantages and Challenges
Efficient Operation: RFID supports batch scanning, capable of reading hundreds of tags simultaneously, which significantly shortens checkout times.
Precise Management: Real-time inventory data combined with a dynamic replenishment system can reduce out-of-stock rates to below 1% while minimizing product loss.
Enhanced User Experience: A fully automated process eliminates the need for waiting in line, and when coupled with personalized recommendation algorithms, it enhances user engagement and retention.
Cost Pressure: Although the cost of passive RFID tags has dropped to between 7 to 15 U.S. cents per tag, large-scale deployment still requires significant investment in hardware such as readers and antenna networks.
Technical Bottlenecks: Metal or liquid packaging can interfere with RFID signals, necessitating optimization in tag design or the adoption of higher frequency technologies to overcome these challenges.
Privacy Concerns: The collection and storage of user behavior data must comply with regulations such as GDPR to prevent information breaches.
4. Industry Outlook
As international organizations like ISO/IEC work toward standardizing RFID technology, the formation of a network of unmanned stores across regions and brands is likely, thereby promoting supply chain collaboration. Future stores are expected to integrate computer vision with RFID technology—for example, Amazon Go’s “multimodal recognition” model leverages sensor fusion to achieve recognition accuracy of up to 99.9%. Furthermore, RFID technology can optimize inventory turnover, reduce food waste, and minimize excessive packaging. Some European supermarkets have even implemented dynamic pricing algorithms to automatically discount products approaching their expiration dates.
RFID-based self-driving stores represent not only an efficiency revolution in retail but also a starting point for reconfiguring the relationships among people, goods, and environments. Despite the challenges of cost and technology, their core value lies in data-driven precision operations that offer seamless services to consumers while helping merchants reduce costs and increase efficiency. In the future, as technologies such as 5G and edge computing mature, this model may become an indispensable component of the smart city ecosystem.