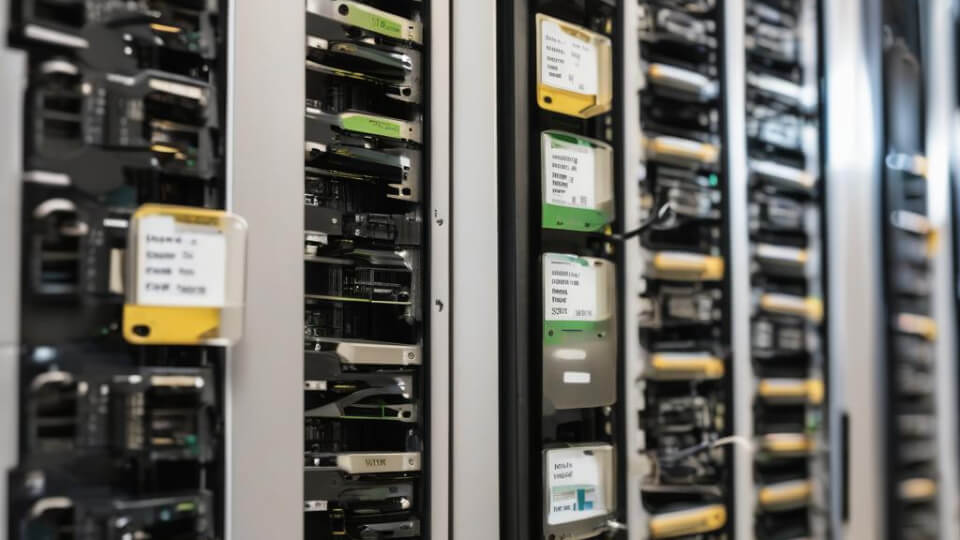
As companies expand their IT infrastructure, IT asset management becomes increasingly complex. Traditional methods of managing assets often face challenges such as slow data updates, frequent human errors, and time-consuming inventory checks, making it difficult to meet the demands of efficient asset management. RFID technology, known for its efficiency, precision, and automation, has emerged as an attractive solution for IT asset management. This article provides a detailed overview of how RFID can be applied to IT asset management, specific implementation steps, and how RFID enables efficient asset management.
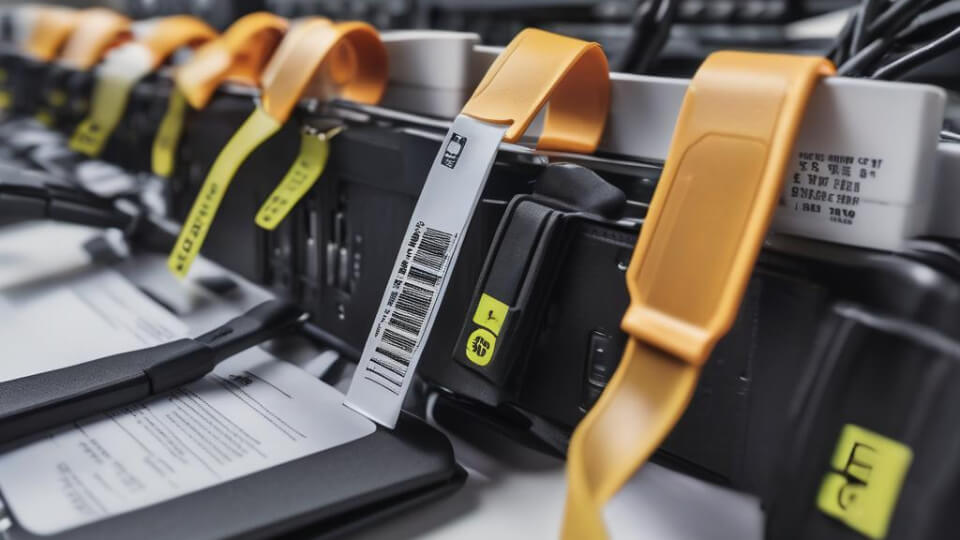

Detailed Applications of RFID in IT Asset Management
IT Equipment Identification and Classification
Each piece of IT equipment (such as servers, switches, laptops, etc.) is assigned a unique RFID tag. The tag stores the equipment’s unique identification code and other relevant information, including equipment type, brand, model, purchase date, etc. This information can be automatically identified and recorded by RFID readers. RFID technology enables fast identification and classification of different types of equipment, especially for large enterprises that need to manage various types of assets.
Location Tracking
RFID allows for real-time tracking of IT equipment. By installing fixed RFID readers in offices or data centers, companies can monitor asset location dynamics in real-time. When equipment is moved, RFID readers automatically detect the tag information and transmit it to the management system. This simplifies asset location tracking, particularly in scenarios where equipment is distributed across different areas and frequently relocated.
Asset Maintenance Management
RFID not only stores basic asset information but also records maintenance schedules and history. When equipment is due for maintenance, the system can automatically send reminders based on the information stored in the RFID tag, ensuring timely maintenance and preventing business interruptions due to equipment failure. Additionally, RFID tags can store maintenance records, which are useful for analyzing faults and making future maintenance decisions.
Inventory and Auditing
Traditional inventory processes often require manually checking equipment serial numbers, consuming significant time and labor. RFID greatly simplifies this process. Asset managers can simply carry a mobile RFID reader and walk through areas where the equipment is located. The reader automatically captures all the equipment tag information and generates an inventory report. This contactless, bulk reading method allows entire offices or data centers to be inventoried in minutes, dramatically improving efficiency.
Theft Prevention and Access Control
RFID can be integrated with security systems to manage asset movement in and out of controlled areas. In offices, data centers, and other facilities, companies can install fixed RFID readers at entry points. If equipment is moved out of an authorized area without permission, the system automatically triggers an alarm. In conjunction with identity recognition technologies, the system can also track who removed the equipment and when, thereby improving asset security.
Asset Disposal and Replacement
RFID can also track the lifecycle of assets, recording the entire process from procurement, use, maintenance, to disposal. When equipment reaches the end of its useful life or requires replacement, the system can automatically alert asset managers based on the historical data stored in the RFID tag. This enables companies to plan equipment replacement cycles more effectively, avoiding both overuse and delayed replacements.
Specific Implementation Steps for RFID in IT Asset Management
Requirement Analysis and Planning
Before deploying an RFID system, companies must conduct a comprehensive requirement analysis to determine the types, quantity, location, and management needs of the IT assets to be tracked. For example, does the company need real-time tracking of all equipment movement, or is periodic inventory sufficient? These needs will define the scale of the RFID system, hardware configuration, and software functionality.
Selecting the Appropriate RFID Tags
Choosing the right RFID tags depends on the material and installation method of the IT equipment. RFID tags generally fall into two categories: flexible anti-metal tags and standard adhesive tags. The size of the tags can be customized based on the specific requirements of the application, such as available surface area for placement, read range, and storage environment. Common sizes include 60*25mm, 54*34mm, and 40*10mm, with thicknesses around 0.3mm to 1.2mm.
Encoding RFID Tags
In IT asset management, RFID tags often use a three-in-one encoding method, combining an asset code, a QR code, and an EPC (Electronic Product Code). For bulk encoding, RFID printers with 203/300/600 dpi resolution can be used. For single encoding, RFID desktop encoders are ideal, allowing for individual tag writing and data modification.
RFID typically supports data integration and can be linked with the company’s existing asset management system to complete RFID tag data generation and registration.
Labeling and Binding IT Assets
RFID tags should be affixed to all IT assets requiring management. To prevent tags from being easily removed or damaged, companies can select durable tag materials and place them in positions that are easy to install, hard to damage, and do not interfere with usage. Tags can be attached to the exterior or interior of the product, provided the read distance requirements are met.
Once labeling is complete, for existing assets, RFID handheld devices can be used to scan both the original asset label and the RFID asset tag, allowing for quick binding and verification. For new assets, this binding can be done during the warehousing process by scanning the tags.
Installing Readers for Access Control
For IT asset location management, companies can define management information such as campus, building, and office area. RFID readers can be installed in the relevant areas to enable access control. Key devices for access control include RFID readers, antennas, infrared sensors, and sound/light alarm systems. If an asset is moved out for travel, loan, sale, or disposal without authorization, an alarm will be triggered, and the system will record detailed entry/exit logs, facilitating traceability.
Testing and Optimization
Thorough testing before the system goes live is critical. Companies can choose specific areas or equipment for a pilot run, testing the signal coverage of the readers, accuracy of tag readings, and system response speed. Based on the test results, necessary adjustments and optimizations can be made to ensure the system operates smoothly and efficiently once fully deployed.
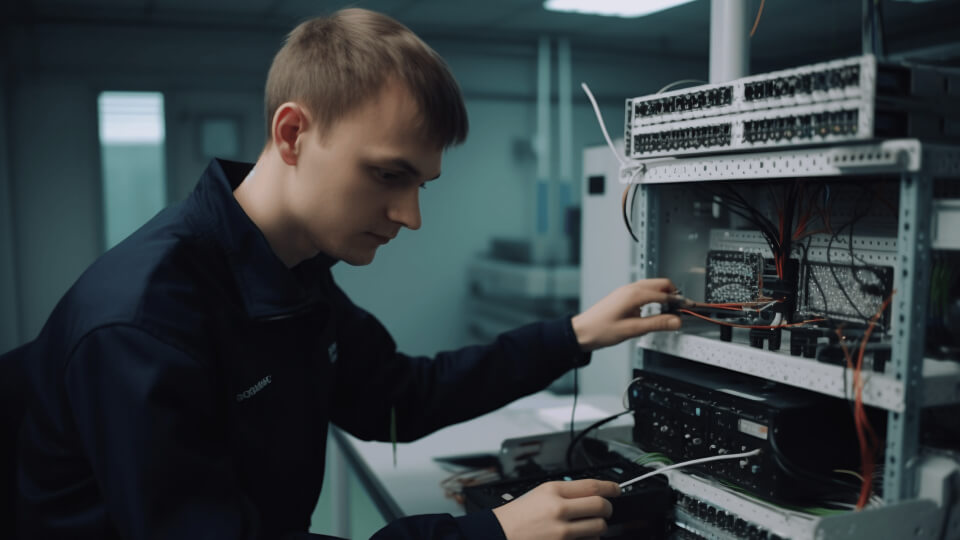

The Importance of RFID in the IT Industry
RFID technology can significantly improve management efficiency, reduce human errors, enhance asset security, and enable automated inventory and maintenance in IT asset management. When implementing RFID systems, companies need to plan carefully based on their specific needs, select the right tags, readers, and software systems, and ensure the system is optimized for effective operation. By successfully implementing RFID, companies can better manage their IT assets, reduce management costs, and increase asset utilization.