Large retail supermarkets face numerous challenges—from managing vast inventories and reducing shrinkage to providing seamless customer experiences across multiple channels. By using radio waves to automatically identify and track items, RFID offers significant improvements over traditional barcode systems, especially in large-scale, complex retail settings.
This guide explores how RFID is deployed in various supermarket zones, the required hardware configurations, and real project examples that highlight its impact.
1. Receiving and Inbound Logistics
Upon arrival at a supermarket, shipments—whether individual cartons or entire pallets—must be quickly and accurately verified. RFID technology streamlines this process by ensuring every item is pre-labeled with durable RFID tags that carry unique identification numbers. Fixed RFID readers positioned at the receiving docks can simultaneously scan all inbound items without needing direct line-of-sight.
Tags: High-performance UHF passive RFID tags that are designed to withstand harsh environments, such as varying temperatures and humidity.
Readers: Fixed readers equipped with omnidirectional antennas are installed at loading docks to quickly capture data from all tags in the shipment.
Systems: Middleware aggregates the data and compares it to purchase orders in real time, automatically updating the ERP system and flagging any discrepancies.
Walmart’s pilot program in its distribution centers is a well-documented case. By using RFID, Walmart improved receiving accuracy from approximately 70% to over 95%, greatly reducing manual errors and speeding up the processing time of shipments. This real-time data capture not only reduces labor costs but also minimizes discrepancies, ensuring that the right products reach the shelves promptly.
2. Warehousing and Inventory Management
In the back-of-house storage areas, efficient inventory management is vital. RFID systems provide continuous, real-time monitoring of stock levels, enabling automated cycle counts and reducing the need for labor-intensive manual counts. With RFID, inventory errors can be minimized, and stock replenishment can be accurately timed.
Tags: Cost-effective indoor RFID labels tailored to various product types (for example, thin tags for apparel and rugged ones for electronics).
Readers: A combination of fixed readers, which provide consistent coverage along storage aisles, and handheld readers for spot-checks and auditing.
Systems: The RFID middleware filters duplicate reads and integrates data with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), ensuring that supervisors receive real-time dashboards and alerts when stock levels deviate from expectations.
Tesco, one of the largest UK supermarket chains, implemented RFID in their warehouses and achieved near 99% inventory accuracy across thousands of SKUs. Their system reduced manual labor by automating inventory updates, which in turn lowered labor costs by up to 15%. This increased accuracy directly contributed to fewer out-of-stock incidents and more efficient stock replenishment processes.

3. Sales Floor and Merchandising
On the retail floor, maintaining accurate inventory levels and ensuring products are readily available for customers is paramount. RFID-enhanced smart shelves and digital displays support real-time monitoring of merchandise. As products are removed or repositioned, RFID readers embedded in the shelves update inventory records automatically.
Tags: Ultra-thin, flexible RFID labels that blend with the product packaging, ensuring they do not disrupt the visual merchandising.
Readers/Antennas: Fixed low-power RFID readers are integrated into the shelves or mounted above display areas. These readers are calibrated to read tags within a short range, thereby minimizing potential interference between adjacent products.
Systems: Data from these readers is funneled into a Retail Management System (RMS), which provides real-time inventory levels, alerts for low stock, and analytics to help manage reordering and shelf restocking decisions.
According to industry expert Kris Barton,
“RFID on the sales floor not only improves inventory accuracy, but also delivers immediate alerts that allow for swift action—a game-changer for real-time merchandising.”
Smart shelves have been demonstrated in pilot projects where on-shelf availability increased from 80% to nearly 98%, significantly improving the shopping experience by ensuring that customers always find what they need.
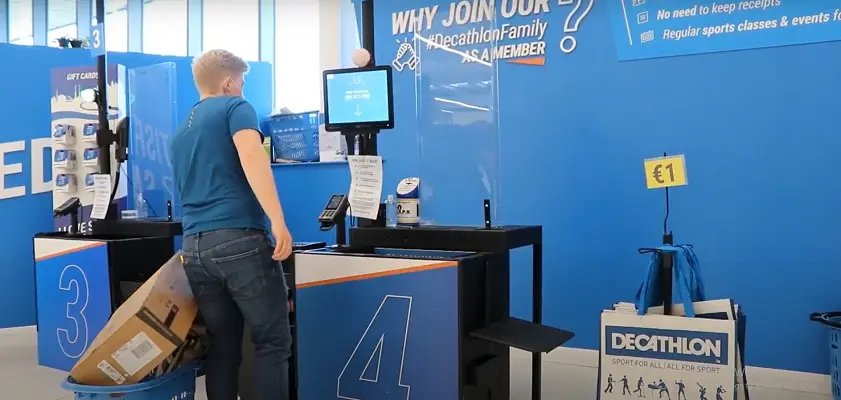
4. Self-Checkout and Customer-Facing Zones
Self-checkout areas are enhanced by RFID technology through the rapid, simultaneous scanning of all items in a customer’s cart. Unlike barcode scanning, RFID does not require manual line-of-sight alignment, thereby speeding up the checkout process and reducing errors. This not only improves customer throughput but also minimizes the potential for theft.
Tags: Every product is tagged with a passive RFID tag that includes essential data such as product ID and price; high-value items may incorporate additional security features.
Readers: Self-checkout kiosks integrate RFID readers with wide coverage antennas capable of scanning an entire shopping basket at once.
Systems: The self-checkout system integrates with the point-of-sale (POS) system to automatically verify transactions in real time. In some implementations, RFID data is cross-referenced with weight sensors at the bagging area to confirm that the items scanned match the expected weight.
Decathlon has deployed RFID-enabled self-checkout systems in several of its stores. Internal data from Decathlon shows that RFID reduced checkout times by nearly 50% compared to traditional barcode systems, thus allowing a smoother, faster customer experience while also reducing losses through more accurate transaction capture.

5. Security and Exit Gate Applications
At security exit gates, RFID ensures that every item leaving the store has been properly accounted for at the checkout. Fixed RFID readers monitor the exit zones, and any discrepancies between the item data and sales records trigger an alarm, alerting security personnel in real time.
Tags: Standard UHF RFID tags are used on most merchandise; for high-risk or high-value items, tags with encryption or anti-cloning features are recommended.
Readers: Exit gate systems typically employ fixed RFID readers with ample coverage across the entire threshold.
Systems: Data from the exit gate readers is continuously cross-referenced with the POS system to detect any unauthorized removals, helping to reduce overall shrinkage.
Retail chains implementing RFID security at exit gates have reported shrinkage reductions of 10%–15%, resulting in significant annual savings and improved loss prevention.
Conclusion
Tailoring RFID solutions for different zones in large retail supermarkets creates a comprehensive, interconnected system that boosts operational efficiency, enhances inventory management, and protects against losses.
As RFID technology continues to evolve and integrate with emerging platforms such as AI and IoT, retailers will be better equipped to anticipate demand, streamline processes, and gain a competitive edge in an increasingly data-driven marketplace.