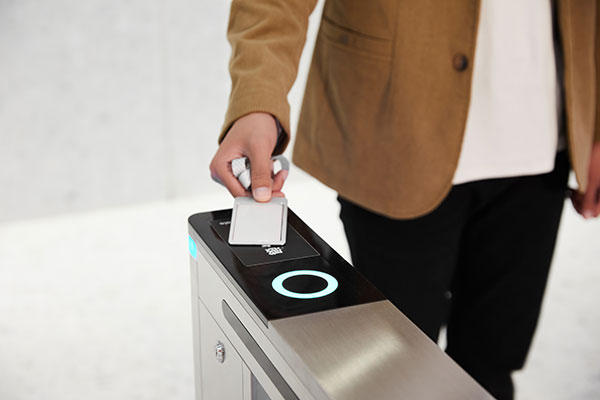
Since the launch of Alipay’s “Tap & Pay” feature in July this year, it has gained widespread adoption for its convenience and efficiency, especially in payment and ordering scenarios. This feature is powered by NFC (Near Field Communication) technology, allowing users to make payments or place orders simply by holding their NFC-enabled smartphone close to an NFC device or table sticker with a “Tap & Pay” symbol—no need to open an app or scan a QR code.
I. “Tap & Pay” for Payments
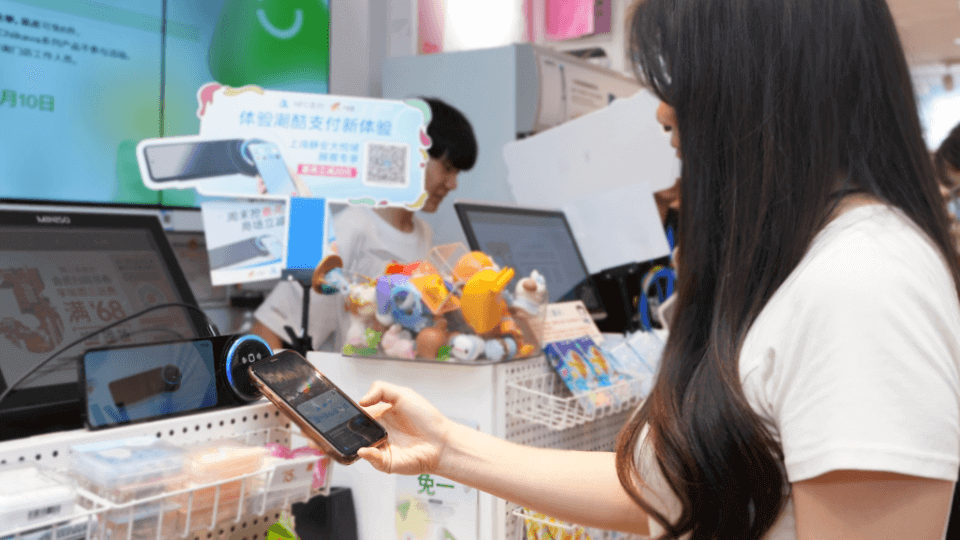

Traditional QR code payment processes often require users to open the payment app, locate the payment code or scanning page, and scan the merchant’s QR code to complete the transaction. In contrast, Alipay’s “Tap & Pay” function allows users to complete payments just by bringing their NFC-enabled smartphone near the merchant’s NFC device. This streamlined process is especially suitable for high-traffic areas where quick transactions are essential, such as subway stations, buses, and convenience stores.
The NFC transmission process is encrypted and uses authentication mechanisms. On top of this, “Tap & Pay” integrates device authentication, fingerprint or facial recognition, and other layered security verifications to ensure users’ payment information remains protected. Additionally, Alipay records each “Tap & Pay” transaction, enabling users to review payment history and manage expenses.
For most smartphone users, “Tap & Pay” presents minimal technical barriers and requires no learning curve. As long as a phone supports NFC functionality, users can easily utilize this feature. Furthermore, this feature has low network dependence, allowing transactions to be completed without continuous internet connectivity.
II. “Tap & Pay” for Ordering

Users can initiate the “Tap & Pay” ordering process by placing their phone close to NFC devices located on tables, at entryway signs, or at ordering stations within a store. This action automatically directs the user to the restaurant’s electronic menu, where they can browse items, place orders, and pay—all without waiting in line or needing assistance from staff.
In the post-pandemic era, the demand for contactless services has increased significantly. With “Tap & Pay” ordering, customers can complete the entire ordering and payment process through their phone, minimizing contact with public surfaces or other people. This feature is particularly advantageous in environments with strict hygiene requirements, such as restaurants and cafés.
During peak times, restaurants may face high volumes of orders, and manual ordering can be inefficient and prone to errors. Alipay’s “Tap & Pay” ordering transmits orders directly to the kitchen system, reducing the time needed for manual entry and ensuring order accuracy. After placing an order, the kitchen or preparation station instantly receives the order details, streamlining service.
III. Fundamentals and Applications of NFC Tags

NFC tags enable wireless, close-range communication and are based on RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) technology. The core principle involves data exchange between devices through magnetic field coupling, activating automatic data transmission when two devices are nearby. In Alipay’s “Tap & Pay” feature, the NFC tag acts as a transmission bridge, facilitating data interaction between the user’s phone and the NFC terminal, enabling quick payment and ordering.
1. Types of NFC Tags
NFC tags can be classified into three main types according to their application:
1.1 Passive Tags: These tags do not contain a power source, relying on the electromagnetic induction from NFC readers to obtain power, and are typically used for simple data storage and transmission, such as electronic labels and business cards.
1.2 Active Tags: Equipped with their own power source, active tags can actively transmit data, making them suitable for more complex data exchange scenarios, such as electronic access cards and public transportation cards.
1.3 Bidirectional Tags: Capable of two-way data exchange, these tags enable the NFC terminal and phone to exchange information, as seen in Alipay’s “Tap & Pay” payment and ordering functions, allowing for quick data transfer and payment processing.
2. Advantages of NFC Tags
– Convenience: NFC tags enable data transmission simply by placing devices nearby, eliminating the need for manual interaction.
– Security: The close-range communication characteristic of NFC tags enhances transmission security. Combined with encryption, they effectively mitigate data theft risks.
– Efficiency: With fast data transfer rates and support for various data formats, NFC technology is ideal for rapid payment and information transmission.
3. Broader Applications of NFC Tags in Other Industries
Beyond payment and ordering, NFC tags offer promising applications across sectors such as healthcare, logistics, and retail.
3.1 Healthcare
In healthcare, NFC tags can be used for patient identification, medication management, and medical equipment tracking. For example, by embedding NFC tags in patient wristbands, healthcare providers can quickly verify patient identities and ensure accurate medication and treatment. Additionally, NFC tags can track medications by recording batch numbers and expiration dates, improving safety and efficiency in drug management.
3.2 Logistics and Supply Chain
NFC tags are widely used in logistics for tracking and inventory management. By embedding NFC tags in goods, warehouse managers can track item location and status in real-time, optimizing storage and transportation processes. Various stages of the supply chain can also utilize NFC tags for information exchange, reducing manual record-keeping errors.
3.3 Retail
In the retail industry, NFC tags are employed for product labeling and inventory management. Consumers can access information about a product’s origin, ingredients, and production date by scanning the NFC tag with their phones. Retailers can also use NFC tags to monitor inventory in real-time, facilitating efficient restocking and management.
IV. Future Development and Challenges for NFC Tags
Although NFC tag technology offers wide-ranging applications in payment, ordering, and beyond, there are still challenges to address:
1. Cost Control
NFC tags are relatively costly to manufacture, especially in large-scale application scenarios. Reducing tag production costs is crucial for wider adoption.
2. User Privacy and Data Security
While NFC tags generally offer secure data transmission, there remains a risk of data breaches. Strengthening encryption and authentication protocols will be necessary to protect user privacy and data security.
3. Standardization of Technology
The market currently faces compatibility issues among various NFC devices and tags, as different brands may not be interoperable. Establishing standardized NFC technology will be essential for broad adoption.
V. Conclusion
Alipay’s “Tap & Pay” payment and ordering functions, based on NFC tag technology, provide a highly convenient and efficient user experience. NFC technology, with its ease of use, security, and rapid data transfer capabilities, is seeing growing adoption not only in payment and ordering but also in healthcare, logistics, and retail. Moving forward, with advancements in technology and reductions in production costs, NFC tags are likely to expand further into various aspects of daily life, promoting a smarter, more connected society. However, to fully integrate NFC technology, the industry must address challenges related to standardization and data security, achieving a robust infrastructure that benefits both consumers and businesses alike.