RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology has revolutionized library operations, particularly in managing book check-in/check-out processes. This article will explore the concept, significance, and practical implementation of RFID in libraries, with a detailed case study of the New York Public Library (NYPL).
Concept and Significance of RFID in Libraries
RFID technology uses radio frequency signals to track and identify objects, in this case, library books. The implementation of RFID for book check-in/check-out processes offers several benefits.
Enhanced Efficiency. RFID eliminates the need for manual scanning, as multiple books can be read simultaneously, enabling faster check-in/check-out processes.
Improved Accuracy. RFID ensures accurate book identification, reducing errors and enhancing overall data integrity.
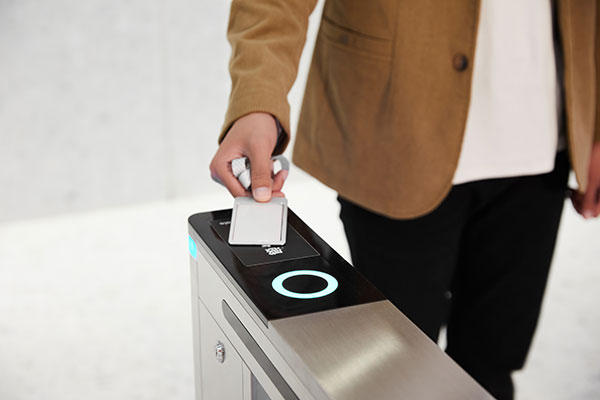
Enhanced User Experience. RFID enables self-service options, allowing library patrons to conveniently check in/check out books without staff assistance.
RFID Implementation at the New York Public Library
The New York Public Library is a prominent example of successful RFID implementation in a large-scale library system. Let’s explore the detailed process.
NYPL conducted extensive research, evaluating the benefits and challenges of RFID implementation. They recognized the potential of RFID to improve operational efficiency and enhance user experience.
They carefully selected RFID tags based on their performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
For tag Installation and Programming, NYPL embarked on a phased approach, initially conducting a pilot project to install and program RFID tags on a select number of books. This allowed them to assess the feasibility and address technical challenges before proceeding with full-scale implementation. Subsequently, they gradually installed RFID tags on the entire library collection, programming and configuring the tags to link with book information in the library management system.
Then in System Integration and testing, NYPL integrated RFID systems with their existing library management software, ensuring seamless data synchronization between RFID readers and the central database. Extensive testing was conducted to ensure the stability and reliability of the RFID system.
Adapting to new workflows and understanding the RFID technology required comprehensive staff training. NYPL invested in training programs to ensure a smooth transition and effective utilization of the RFID system.
RFID implementation at NYPL yielded remarkable outcomes.
RFID technology significantly expedited the book check-in/check-out process, reducing transaction time and minimizing waiting periods for library patrons.
Real-time tracking of books enabled efficient inventory management, ensuring accurate stock information and minimizing loss or misplacement.
The user-friendly self-service options empowered library patrons, resulting in increased user satisfaction and engagement.
The Future of RFID in Libraries
Challenges and Overcoming Obstacles
The implementation of RFID in libraries may face certain challenges. Mainly refers to the cost of RFID implementation, including tags, readers, infrastructure upgrades, and staff training, which can be substantial.
But all practitioners believe the future prospects of RFID in libraries are promising. With the advancement of RFID technology, such as smaller and more affordable tags, increased read ranges, and improved compatibility, will further enhance its capabilities. RFID will continue to play a vital role in optimizing library operations and meeting the evolving needs of library users.